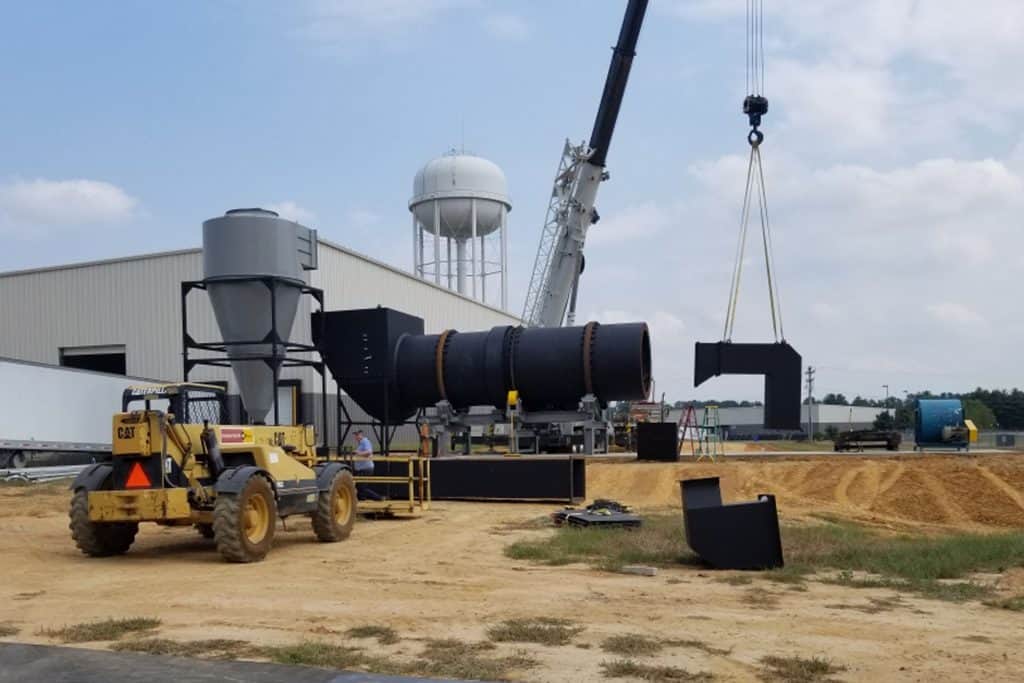
Industrial dryers stand as essential equipment in numerous manufacturing processes, particularly in the drying of bulk solids such as grains, minerals, and chemicals. This article delves into the operational principles, mechanisms, and diverse applications of industrial dryers across various industries.
Industrial dryers serve the critical function of reducing the moisture content in bulk solids through the application of heat and airflow. Unlike other types of dryers, rotary dryers feature a rotating drum or cylinder, which facilitates efficient drying by exposing the material to hot air as it tumbles within the cylinder. These dryers are renowned for their versatility, reliability, and ability to handle a wide range of materials.
Read: How Much Do Industrial Dryers Cost?
Operational Mechanisms of Industrial Dryers
The functionality of industrial dryers hinges on the principles of convective heat transfer and moisture evaporation. The operational mechanisms of rotary dryers can be summarized as follows:
Heat Transfer: Industrial dryers employ hot air or gas as the drying medium, which is introduced into the rotating drum. The heat energy is transferred to the wet material through direct contact with the heated drum surface.
Material Movement: As the drum rotates, the material inside is lifted by the flights or lifting bars attached to the inner surface of the drum. This tumbling action exposes the material to the hot air, ensuring uniform drying and preventing agglomeration or overheating.
Moisture Evaporation: The heat energy supplied to the material causes the moisture or solvent to evaporate, effectively reducing the moisture content of the material. The evaporated moisture is then removed from the dryer chamber by the airflow or venting system.
Types of Industrial Dryers
Industrial dryers come in various configurations to accommodate different materials and processing requirements. Some common variations include:
Direct Rotary Dryers
In direct dryers, the hot air or gas is introduced directly into contact with the material being dried, ensuring efficient heat transfer and rapid moisture removal.
Indirect Rotary Dryers
Indirect dryers utilize an external heat source to heat the drying medium, which is then circulated through the drum to dry the material indirectly. This method is preferred for heat-sensitive materials or applications requiring inert atmospheres.
Counter-Current Rotary Dryers
In counter-current dryers, the material and the drying medium flow in opposite directions, maximizing the contact time between the material and the hot air for thorough drying.
Co-Current Rotary Dryers
Co-current dryers feature parallel flow of the material and the drying medium, offering high thermal efficiency and shorter residence times.
Applications of Industrial Dryers
The versatility and efficiency of industrial dryers render them indispensable across a wide range of industries. Some key sectors where industrial dryers find extensive applications include:
1. Minerals and Mining
Industrial dryers are utilized to dry ores, concentrates, and mineral sands before further processing or transportation, enhancing product quality and reducing transportation costs.
2. Chemical Industry
Dryers play a crucial role in chemical manufacturing by drying various chemical intermediates, fertilizers, and specialty chemicals to precise moisture levels.
3. Agriculture
Industrial dryers are employed in the agriculture sector for drying grains, seeds, and agricultural products, ensuring proper storage conditions and preventing mold growth.
4. Environmental Remediation
Dryers are utilized in environmental remediation projects for drying contaminated soil, sludge, or waste materials, facilitating safe disposal or recycling.
Looking to Install an Industrial Dryer?
Industrial dryers stand as indispensable equipment in manufacturing processes across diverse industries, offering efficient and reliable drying solutions for bulk solids. Through their unique operational mechanisms and versatile configurations, dryers facilitate thorough moisture removal while maintaining product integrity.
With applications ranging from minerals and mining to chemical manufacturing, agriculture, and environmental remediation, industrial dryers contribute significantly to enhancing product quality, reducing costs, and improving overall efficiency in manufacturing operations.